Mirror 3x3x3 Cube Tutorial
The Mirror 3x3x3 Cube is a fascinating puzzle that functions similarly to the standard 3x3x3 cube but adds an extra level of complexity by using pieces of varying sizes instead of color. When scrambled, the cube changes its shape, making it look more complex. The goal is to restore the cube back to its original cubic form, with all layers aligned.
Introduction
- Mirror Cube Basics: Unlike a regular 3x3x3 cube, the Mirror Cube does not rely on color-matching but instead on aligning pieces of different sizes. Each piece has a unique height, width, or depth that determines its correct position.
- Challenge of Shapeshifting: When scrambled, the cube distorts into various shapes. Solving it requires spatial awareness and an understanding of size differences.
Step-by-Step Solution for the Mirror 3x3x3 Cube
Step 1: Understanding the Notation
The Mirror 3x3x3 Cube uses the same notations as the regular 3x3x3 cube:
- R (Right), L (Left), U (Up), D (Down), F (Front), B (Back)
- Clockwise (no symbol): Turn the face clockwise.
- Counterclockwise ( ‘ ): Turn the face counterclockwise.
- Double Turn (2): Turn the face 180 degrees.
Step 2: Solving the First Layer (Cross)
- Choose a Reference Piece:
- Start by selecting the largest piece on the cube. This will be your fixed reference corner, which represents the “white center” in a regular 3x3x3 cube.
- Form the Cross:
- Identify the four edge pieces that will align with your chosen reference center. Each of these pieces must match in size and shape with the center piece.
- Position each edge piece next to the reference piece to form a cross. You may use the following algorithm to place the edges correctly:
- Algorithm to Insert Edges: F R U R’ U’ F’ (to insert edges from the middle layer)
- Align the Cross with the Center:
- Ensure that all the edge pieces are aligned correctly with the center piece, forming a cross shape with the appropriate sizes.
Step 3: Solving the First Layer Corners
- Position the Corners:
- Find the corner pieces that belong to the first layer. The corner pieces will have unique sizes that fit between the center and edge pieces.
- Use the following algorithm to insert each corner into its correct position:
- Algorithm for Corner Insertion: U R U’ R’
- Repeat for All Corners:
- Continue inserting corners using the algorithm until all first-layer corners are in place, forming a flat, cubic shape on the first layer.
Step 4: Solving the Second Layer
- Identify and Position the Second-Layer Edges:
- Turn the cube upside down so that the solved layer is now on the bottom.
- Look for pieces on the top layer that belong in the second layer. Match the appropriate edges to the center pieces of the second layer.
- Use the following algorithms to move pieces from the top layer to the correct position in the second layer:
- Left Insertion: U’ L’ U L U F U’ F’
- Right Insertion: U R U’ R’ U’ F’ U F
- Continue Until the Second Layer is Solved:
- Repeat these steps until all four edge pieces in the second layer are correctly positioned.
Step 5: Solving the Last Layer (Top Layer)
- Orient the Last Layer Edges:
- Begin by orienting the edges of the last layer. Look for an “L” shape, a straight line, or a cross on the top layer. Use these algorithms to orient the edges:
- Form the Cross: F R U R’ U’ F’
- Complete the Cross: U R U2 R2 U’ R2 U’ R2 U2 R
- Begin by orienting the edges of the last layer. Look for an “L” shape, a straight line, or a cross on the top layer. Use these algorithms to orient the edges:
- Permute the Last Layer Corners:
- Position the last layer corners correctly. Hold the cube so that the piece that needs to be swapped is at the top-right corner.
- Use the following algorithm to cycle three corners:
- Algorithm for Corner Permutation: U R U’ L’ U R’ U’ L
- Orient the Last Layer Corners:
- Finally, orient the corners to solve the cube. Use the following algorithm:
- Algorithm for Corner Orientation: R U R’ U’ R’ F R F’
- Finally, orient the corners to solve the cube. Use the following algorithm:
Step 6: Final Adjustments to Restore Cube Shape
- Fine-Tune the Shape:
- Check if any pieces are slightly out of alignment. If so, use basic moves to rotate them into their correct positions.
- Continue using basic algorithms until the cube is restored to its perfect cubic shape.
Additional Notes for Solving the Mirror 3x3x3 Cube:
- Piece Size Recognition:
- Focus on recognizing the size and shape of each piece. Unlike color cubes, this is crucial for placing pieces in their correct spots.
- Patience with Shapeshifting:
- Due to its shape-shifting nature, solving the Mirror 3x3x3 Cube can be challenging at first. Be patient with recognizing patterns and alignments.
- Practice Basic Algorithms:
- Familiarize yourself with the standard algorithms for a 3x3x3 cube, as they are equally applicable here.
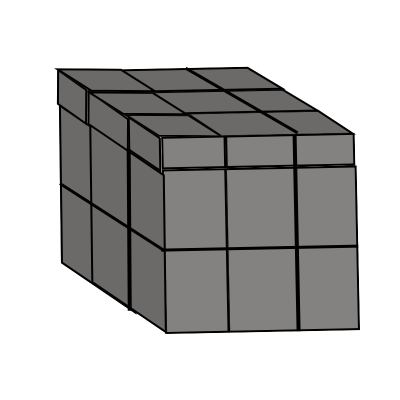
Conclusion:
By following this method and using the size and shape of the pieces to guide your placements, you can solve the Mirror 3x3x3 Cube. Remember to use algorithms carefully, keep track of which pieces are in place, and adjust return the cube to its original shape.
